What is confined space?
What is confined space. It is any area not designed for continuous occupation, which has limited means of entry and exit or is difficult to access. Below are some characteristics of confined space:
Atmosphere without air renewal that may present gas formation or oxygen deficiency. Or that it may develop a poor oxygen atmosphere over time. These are spaces that can present the presence of gases and contaminants. They are spaces that do not have natural ventilation.
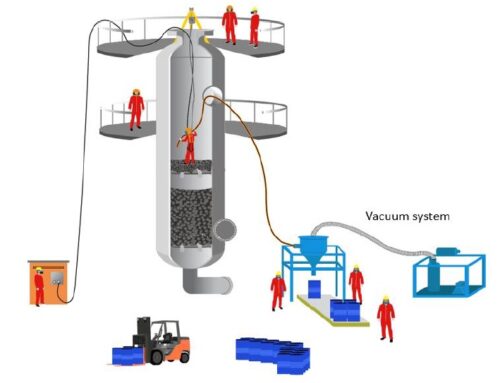
What are confined spaces? Ventilation hoses provide air and exhaust toxic vapors during confined space entry. A guardrail would also be necessary to protect workers from potential falls. Many workplaces contain areas that are considered “confined spaces” because while they are not necessarily designed for people, they are large enough for workers to enter and perform certain jobs. A confined space also has limited or restricted means for entry or exit and is not designed for continuous occupancy.
Confined spaces include, but are not limited to, tanks, vessels, silos, storage bins, hoppers, vaults, pits, manholes, tunnels, equipment housings, ductwork, pipelines, etc. OSHA uses the term “permit-required confined space” (permit space) to describe a confined space that has one or more of the following characteristics: contains or has the potential to contain a hazardous atmosphere; contains material that has the potential to engulf an entrant; has walls that converge inward or floors that slope downward and taper into a smaller area which could trap or asphyxiate an entrant; or contains any other recognized safety or health hazard, such as unguarded machinery, exposed live wires, or heat stress.
Where are confined spaces found?
- Pulp and paper industry;
- Food industry;
- Rubber industry;
- Storage tanks and silos for products of any kind;
- Leather industry;
- Naval industry;
- Chemical, petrochemical and oil refining networks;
- Sewer, gas, water and underground telecommunications services;
- Civil construction;
- Steel and Metallurgical;